What is Asherman’s Syndrome?
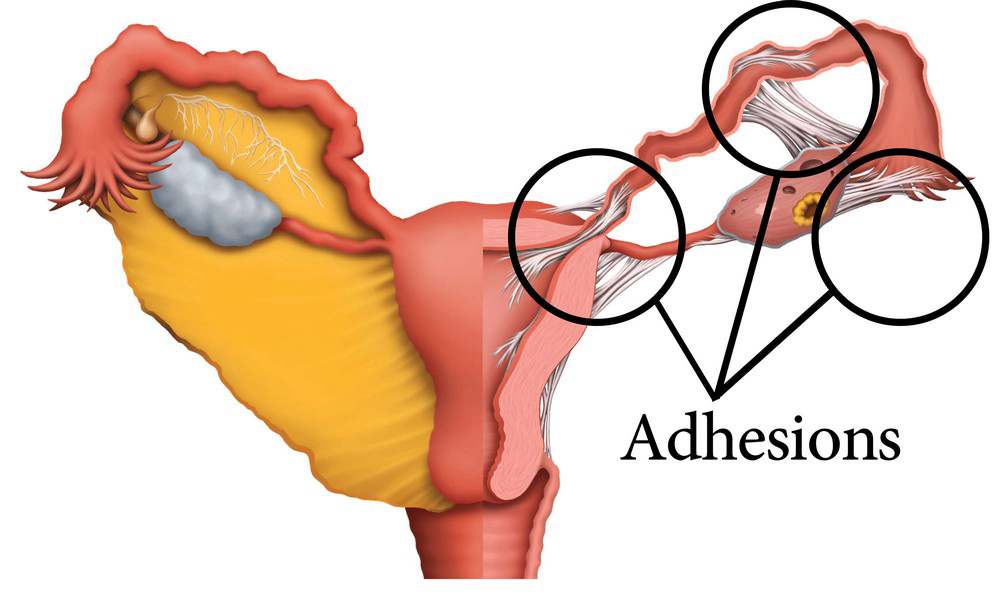
Asherman’s Syndrome is a condition characterized by the formation of adhesions or scar tissue within the uterus. These adhesions, also known as intrauterine adhesions or uterine synechiae, can vary in severity and extent, potentially affecting a woman’s menstrual cycle and fertility.
Uterine Synechiae in Pregnancy
Uterine synechiae can have significant implications for pregnancy. In some cases, they may:
- Interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg
- Increase the risk of miscarriage
- Lead to complications during pregnancy, such as placenta accreta
- Causes difficulties during labor and delivery
How common is Asherman’s syndrome?
While the exact prevalence of Asherman’s Syndrome is difficult to determine due to varying diagnostic criteria and potential underreporting, it is estimated to affect approximately 1.5% of women who undergo hysteroscopy. However, the incidence can be higher in certain populations, particularly among women who have undergone multiple uterine surgeries.
Symptoms and Causes of Asherman’s Syndrome
Asherman Syndrome Causes
The primary causes of Asherman’s Syndrome include:
- Uterine surgery, especially dilation and curettage (D&C)
- Postpartum or post-abortion infections
- Cesarean sections
- Myomectomy (fibroid removal surgery)
- Endometrial ablation
- Pelvic radiation therapy
Symptoms of Asherman Syndrome
Signs of Asherman Syndrome can vary but often include:
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods)
- Hypomenorrhea (light or infrequent periods)
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Infertility
- Cyclic pelvic pain
Symptoms of Scar Tissue in the Uterus
Scar tissue in the uterus can manifest through various symptoms:
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Severe cramping or pelvic pain
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy
Read “How to Tell if You Have Adhesions After C-Section” for more details on cesarean section scar tissue.
Can Asherman’s Syndrome Cause Weight Gain?
While Asherman’s Syndrome itself does not directly cause weight gain, hormonal imbalances associated with the condition may lead to changes in weight. Additionally, the emotional stress of dealing with fertility issues can sometimes contribute to weight fluctuations.
Who gets Asherman’s syndrome?
Asherman’s Syndrome can affect women of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed in women of reproductive age who have a history of uterine surgery or infection and seem to have a difficult time maintaining a pregnancy.
How common is Asherman’s Syndrome after D&C?
The risk of developing Asherman’s Syndrome after a D&C procedure varies depending on the circumstances:
- After a single D&C, 16% risk
- After multiple D&Cs, up to a 32% risk
- Following a postpartum D&C, up to a 40% risk
Is Asherman’s Syndrome genetic?
There is currently no strong evidence to suggest that Asherman’s Syndrome has a genetic component. The condition is primarily associated with acquired factors such as uterine surgery or infection.
How is Asherman’s syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Asherman’s Syndrome typically involves:
- Hysteroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity
- Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): An X-ray procedure that can reveal the shape of the uterine cavity and any adhesions
- Sonohysterography: An ultrasound technique that uses a saline solution to enhance visualization of the uterine cavity
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In some cases, to provide detailed images of the uterus and surrounding structures
- Read our article on “Do Abdominal Adhesions Show on an MRI Scan?”
How is Asherman’s syndrome treated?
Treatment for Asherman’s Syndrome aims to restore the normal structure and function of the uterine cavity. Options include:
- Hysteroscopic Adhesiolysis: Surgical removal of adhesions using hysteroscopy
- Hormonal Therapy: Estrogen supplementation to promote endometrial regrowth
- Barrier Methods: Use of intrauterine devices or balloons to prevent re-adhesion
- Stem Cell Therapy: Emerging experimental treatments using stem cells to regenerate endometrial tissue
- Follow-Up Care: Regular monitoring and potential repeat procedures to prevent recurrence
- Wurn Technique: This involves no surgery or drugs
Clear Passage Physical Therapy and the Wurn Technique
An innovative and non-invasive approach to treating Asherman’s Syndrome is the Clear Passage Physical Therapy using the Wurn Technique. This manual therapy method was developed by Belinda Wurn, PT, and Larry Wurn, LMT, as a result of their personal experience with adhesion-related pain.
Improving the Uterus

In the LEFT IMAGE (Before Therapy) dye shows the inner walls of a uterus that is quite narrowed, squeezed by adhesions (in red circle). This woman will have more difficulty conceiving or carrying a baby to full term, with a greater risk of miscarriage.
In the RIGHT IMAGE (After Therapy), dye now fills her uterus, freed from constricting adhesions (in green circle). The increased mobility creates a much more relaxed organ, more capable of accepting an implanted embryo and carrying it to full term.
How does Clear Passage Physical Therapy work?
The Clear Passage Approach is a specialized form of hands-on physical therapy designed to address adhesions and restrictions in the body’s connective tissues, known as fascia. The therapy employs over 200 manual techniques, including the Wurn Technique, which aims to:
- Deform and detach the bonds of adhesions
- Restore normal, pain-free function of reproductive organs
- Improve fertility by addressing structural issues caused by adhesions
Benefits of Clear Passage Physical Therapy for Asherman’s Syndrome
- Non-Invasive: Unlike surgical procedures, this therapy doesn’t require incisions or anesthesia
- Drug-Free: The treatment doesn’t rely on medications, reducing the risk of side effects
- Holistic Approach: Therapists evaluate and treat the entire body, addressing underlying issues that may contribute to adhesion formation
- Potential for Improved Fertility: Published studies have shown increased pregnancy rates in women who underwent Clear Passage Therapy
What to expect during treatment
Clear Passage Therapy is a treatment program over a series of sessions usually performed within a week, with each session lasting around 3-5 hours per day. A full treatment course usually involves about 20 hours of therapy. During these sessions, skilled therapists use their hands to manipulate fascial tissues, gradually breaking down adhesions and restoring normal tissue mobility.
Scientific Evidence
The effectiveness of Clear Passage Therapy has been documented in several peer-reviewed medical journals. For instance, a study published in the journal “Fertility and Sterility” in 2004 found that women with a history of infertility who underwent Clear Passage Therapy experienced a significant increase in pregnancy rates.
In conclusion, Asherman’s Syndrome is a complex condition that can significantly impact a woman’s reproductive health. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, including innovative approaches like Clear Passage Physical Therapy, are crucial for improving outcomes and preserving fertility.
Contact Clear Passage Physical Therapy today to learn more about how we can help you overcome abdominal pain and regain your health naturally.