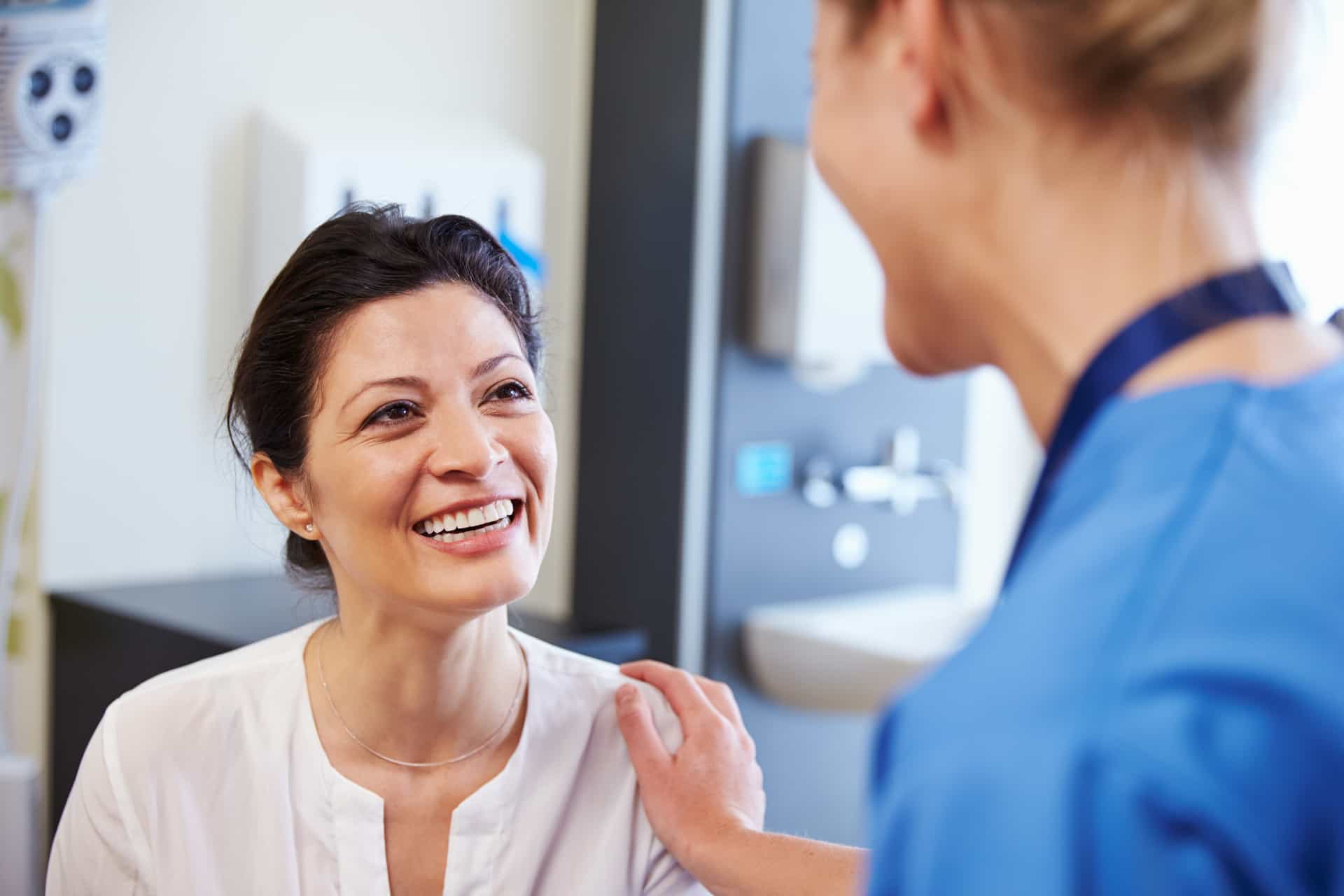
Discover relief from C-section adhesions with Clear Passage Physical Therapy’s free consult and request info, offering a non-surgical approach to address symptoms like chronic pain, infertility, and digestive issues that may have been troubling you for years and are caused by these adhesions. To learn more about getting help visit our Apply to Therapy page.
Table of Contents
C-sections are one of the most common surgeries in the U.S. For many women a c-section isn’t a choice — it is the only safe way to deliver the baby. Most c-section are routine and go as planned. However, many women are unaware of the post-surgical complications that can occur months or even years after a C-section. When the body heals from the procedure, it forms bands of internal scar tissue called adhesions. Adhesions can cause a host of problems if left untreated, including chronic pain, female infertility and life-threatening bowel obstructions. Unfortunately, they are often misdiagnosed because adhesions and pelvic adhesions do not appear on diagnostic tests such as x-rays.
Many of us know about the scar that is left after c-section, but you may be surprised to learn that the way your scar looks can be an indication of your internal healing. Research now suggests that there is a strong correlation between the physical characteristics of an external c-section scar and the adhesions underneath it. Women can use researchers’ findings to help determine whether they have adhesions after a c-section.
What are adhesions?
C-section scar tissue is strands of collagen that form in the body after a surgery, trauma, infection or inflammation. Unfortunately, they are rarely discussed and many patients have never heard the term ‘adhesions.’ Because they are part of the body’s natural healing process, there is no way to prevent adhesions from forming and the surgeries designed to remove them cause more to form.
Adhesions can look like spider webs covering the organs or like filmy, white strands of nylon rope constricting structures inside the body. These powerful strands of collagen wrap around structures at the healing site and can restrict blood flow or reduce the function of internal organs. They can bind tissues and organs, resulting in mild to excruciating pain.
Symptoms of Post C-Section Adhesions and Scar Tissue
When we talk to patients, they often have an ‘aha moment.’ We begin describing what someone with post-surgical adhesions typically experiences and the common response is “Wow, you’re describing me!” Women who have had c-section often know something is wrong – they can feel it, whether is a specific pain or a tightness that they have trouble describing. Unfortunately, many physicians will tell them that pain after c-section is common and that there is nothing to be done about it.
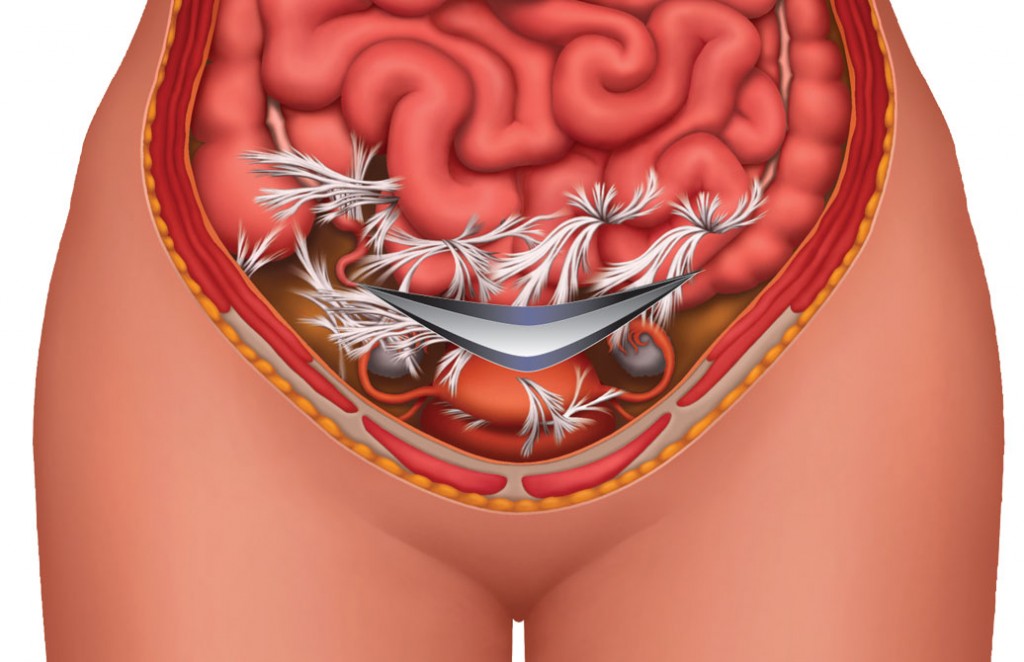 The following are common symptoms of adhesions after a c-section. If these describe you, you may have adhesions.
The following are common symptoms of adhesions after a c-section. If these describe you, you may have adhesions.
- Non-diagnosable abdominal pain (sometimes years after your c-section)
- Trouble standing up straight
- Swollen/bloated abdomen
- Pain during intercourse
- Painful bowel movements
- Secondary infertility
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Increased menstrual pain (since c-section)
- Pain/tenderness at the location of your scar
- Swelling after c-section
- c-section scar pain
Now that you are familiar with the symptoms of post c-section adhesions, we will look at the different visual characteristics of a c-section scar and what it can tell you about the presence of adhesions.
How to Tell if You Have C-Section Scar Tissue
Lay flat on your back and examine your c-section scar. Women with flat, small scars without significant pigment changes (changes in skin color) are less likely to have adhesions in their pelvis. However, a scar that pulls towards the back (indented) or one that is raised and thick — with or without changes in the color of the skin in that area — suggests the presence of dense adhesions. Additionally, women with scars that are darker in color than the rest of their skin are are much more likely to have adhesions, regardless of whether the scar indents, lays flat or protrudes out.
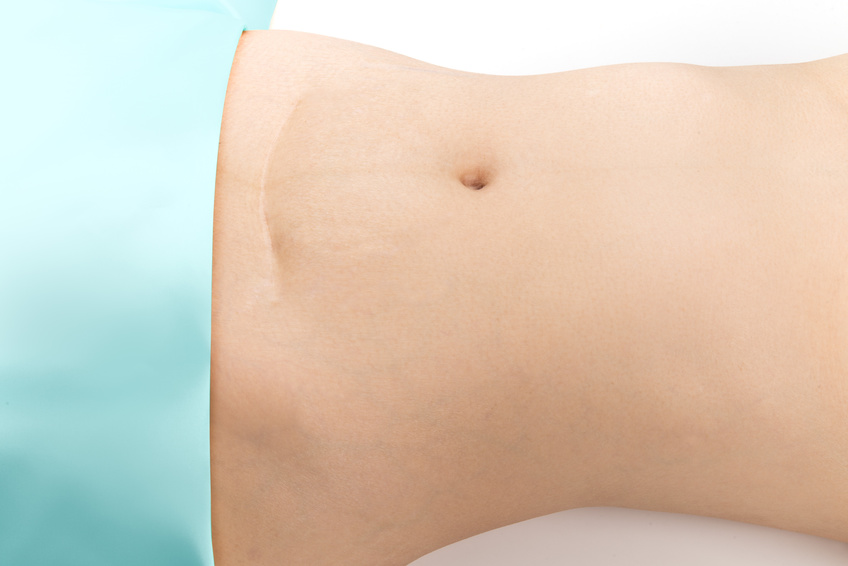
If your scar looks like the example above — indented without any changes to the pigment — there is a high probability that you have adhesions. Because the skin is indented, women with this type of scar are more likely to have dense adhesions than those whose scar looks similar but is flat, without indentation. If you have c-section scar pain you most likely also have c-section scar tissue.
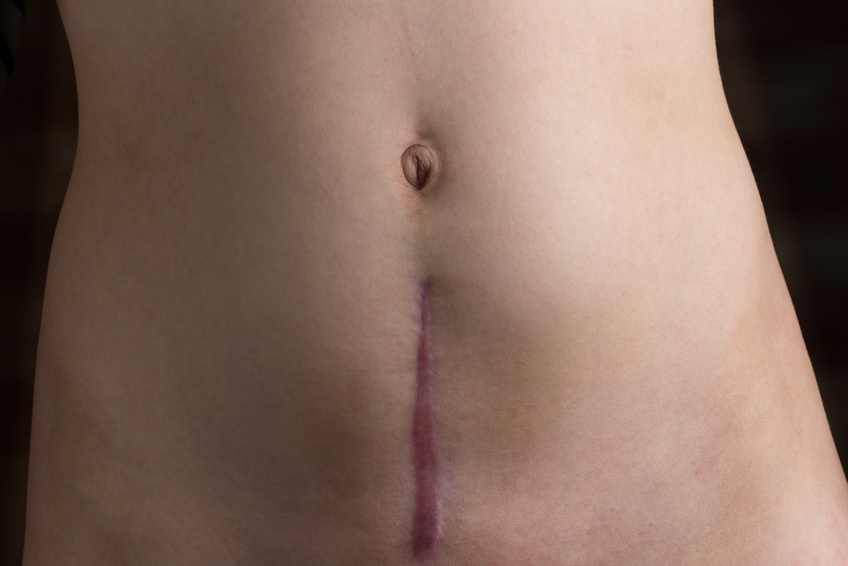
If you scar looks similar to this second image above (raised with pigment change), you also likely have adhesions. Women with this type of scar are most likely to have dense adhesions, which cause pain and dysfunction, because the scar exhibits characteristics from both risk categories — raised and different pigmentation than the surrounding skin.
What to Do if You Think You Have Adhesions
If your symptoms match those described in this article and your scar resembles the examples provided, there is a high probability that you have adhesions. Few options exist for women with abdominal adhesions after a c-section. Surgeons can cut or burn (lyse) adhesions, but the invasive procedure leads to the formation of new adhesions. Some women are able to live without treatment, while others experience recurring, debilitating pain and dysfunction.
If you or a woman you know is suffering from adhesions after a c-section, we encourage you to fill out a contact form or call us at 1-352-336-1433. You will be able to schedule a phone consultation with one of our certified therapists, at no cost, and learn whether our non-surgical treatment is appropriate for you.
References:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25304098
Related Content:
- Prior C-Section Can Cause Adhesions
- The Appearance of a C-Section Scar Can Provide Clues About Abdominal Adhesions
- How to Tell if You Have Adhesions After C-Section ( C-Section Scar Tissue)
- C-Section Pain
- Why Do I Have Pain After C-Section?
- Study Points to Link Between C-Section and Adhesions
Blog Categories: